Virtual production with Subhankar Dutta

For Subhankar Dutta a.k.a Shubie, his prosperous profession began as a passion for the arts. Graduating with an honors in Physics and switching paths to pursue Animation and Film Design, we follow his journey through the bustling city of London into the sets of various virtual productions.
AG: Hello Subhankar, tell us about yourself.
Hello there!
I am Subhankar Dutta, also known as Shubie. I've had a lifelong passion for the arts, particularly drawing, painting, and Hindustani Classical Music. After graduating in Science with honors in Physics, I faced a crucial decision between pursuing arts or science. Inspired by the success of some seniors who attended ZICA Studios in Mumbai for animation, I chose to follow their path. From 2004 to 2007, I studied Animation Film Design at ZICA Studios, learning 2D/3D animation and storytelling from some of India's and abroad's finest Animation Designers. My journey began with an apprenticeship at Rhythm n Hues, a Hollywood Studio, where I started animating. However, my passion for the entire creative process led me to focus on pre-production design, including concept art, character designs, and storyboarding.
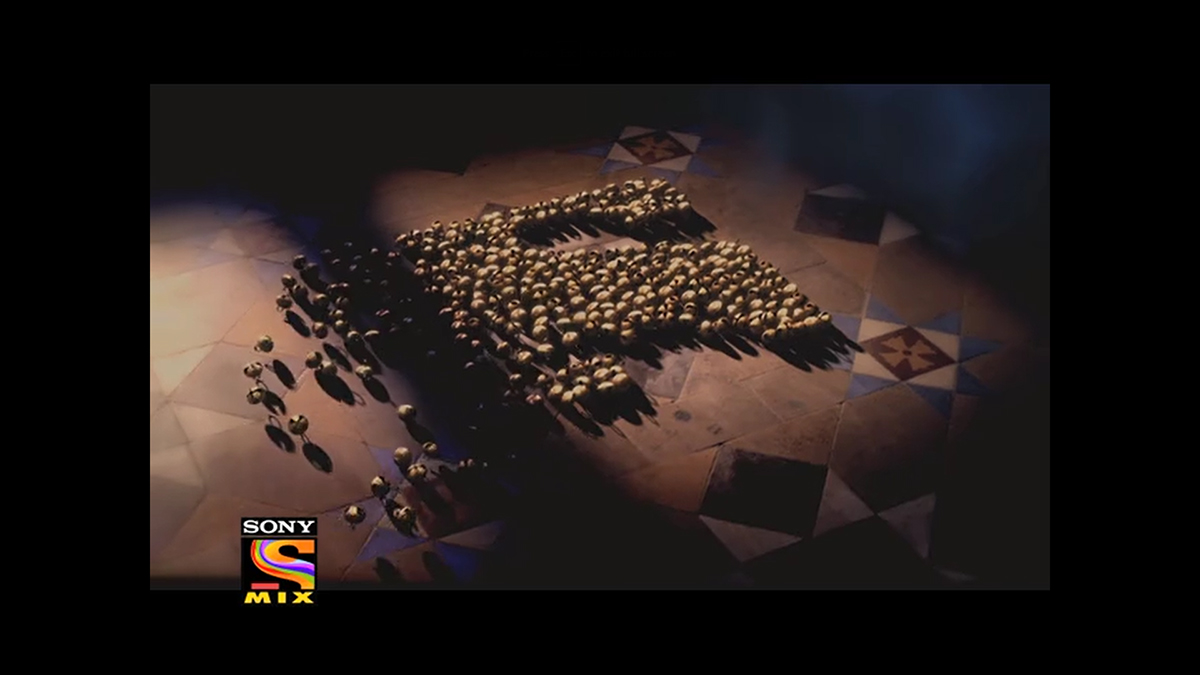

The Danseuse IDENT Conceptualised and directed by Shubbie for Sony Mix.
Over the years, I've been fortunate to work with talented artists and technicians across various studios in India, gaining experience in VFX and animation. I later transitioned into directing music videos, title sequences for Bollywood films, TV commercials, and promos for channels like Sony.

Inspired by legendary filmmakers like Satyajit Ray and Miyazaki, I decided to move to London with my animator wife to collaborate with artists worldwide and explore diverse storytelling approaches. Though challenging at first, I established connections and got involved in various projects, constantly learning in this vibrant cultural hub.
To stay ahead in the rapidly evolving industry, I embraced cutting-edge technology and immersive storytelling. After a Fellowship Program with Epic Games, I worked on fascinating projects, including Lion King 2 (Under Production), using Unreal Engine. As a VP Supervisor, I now collaborate with Hollywood filmmakers and cinematographers, translating, their visions into captivating realms through Realtime Filmmaking. This journey has been an incredible experience of growth and learning as an artist, technician, and creative.
AG: Can you provide an overview of your career path in the virtual production world? How did you get started, and how has your role evolved over the past so many years?
My career path in the virtual production world has been an exciting journey filled with new experiences and technological advancements. It all began when I dabbled with game engines, specifically Unity, for previz work on an immersive project for Castrol Edge with Unit 9 in London back in 2016. This marked my initial exposure to the distinct approach of game engines in contrast to traditional 3D animation and VFX pipelines.

A title sequence, directed by Shubie and produced by Illuminati Films for “Agent Vinod” a Bollywood Spy Film.

During the COVID pandemic, I found time to write some of the long-format story ideas I had in mind. While presenting these ideas to Production Houses and OTT Platforms, I realized the importance of creating impressive dockets and short previews/trailers to effectively communicate my vision. This quest for powerful tools led to a significant turning point in my career when I received a call from Epic Games, offering me a Fellowship in Virtual Production using Unreal Engine.
The fellowship experience was eye-opening as I created a short film called "Break Open," which exposed me to the fascinating capabilities of Unreal Engine. It allowed me to quickly build worlds and bring characters to life in a photorealistic manner without the extensive labor and large teams usually required in traditional animation and VFX. With this newfound ability, my dockets became more impressive, enabling better communication of my ideas to commissioners and enhancing my potential to earn new projects.

I frequently experimented with Unreal Engine, creating small shorts and sequence ideas with photorealistic renders, often incorporating character animations from existing mocap libraries. Sharing these experiments on platforms like LinkedIn caught the attention of professionals in the industry, leading to various project opportunities.
In 2021, I had the opportunity to Art Direct for an immersive project for the Mayor of London, a research project for Royal Holloway London, work on previz for a TV Commercial, and eventually, I joined a leading studio in London that aimed to use Unreal Engine for Lion King 2.
My desire to return to the shoot floor and focus more on the in-camera visual effects (ICVFX) side led me to join DNEG, where I currently serve as a VP Supervisor. In this role, I collaborate closely with the core Creative team, including the Director, Director of Photography (DoP), Production Designer, and VFX Supervisor, to bring their vision to life using advanced technologies such as LED Walls, Simulcam, VolCap, and Performance Capture.
In this phase of my journey, virtual production and Unreal Engine have been instrumental in revolutionizing how I approach storytelling and bring imaginative worlds to fruition. The rapid and powerful capabilities of this technology have opened up new possibilities, allowing me to elevate my craft and create compelling visual experiences.
AG: How have you seen virtual production and the use of Unreal Engine evolve and transform over the course of your career?
Throughout my career, I have witnessed a remarkable evolution and transformation in virtual production and the use of Unreal Engine. The advancements have been profound, revolutionizing the way storytelling is complemented, and traditional VFX is enhanced.
One of the most significant changes has been the tremendous growth in ease of use and the potential of virtual production as a storytelling tool. Unreal Engine has continually improved its interface and features, making it more accessible to creators with varying levels of expertise. As a result, filmmakers and artists can now leverage virtual production techniques more effectively to bring their visions to life.
The strides made in high-fidelity rendering have been awe-inspiring. Unreal Engine has evolved to deliver stunning visuals, pushing the boundaries of what is achievable in real-time rendering. This has enabled filmmakers to create immersive and photorealistic worlds, enhancing the overall cinematic experience.
Additionally, the seamless inter-operability between various Digital Content Creation (DCC) applications has been a game-changer. The ability to import and export assets from different software tools within Unreal Engine streamlines the production pipeline and facilitates collaboration among artists and departments.
Handling massive amounts of data has become much more manageable, thanks to the power of hardware components like GPUs. This has allowed for more complex and detailed scenes, enabling filmmakers to create grandiose worlds and breathtaking visual effects.
The integration of digital humans has been another groundbreaking development. Features like Metahumans have opened up new avenues for realistic character creation, reducing reliance on manual modeling, texturing, rigging, and animation. This not only saves time but also increases the efficiency of the production process.
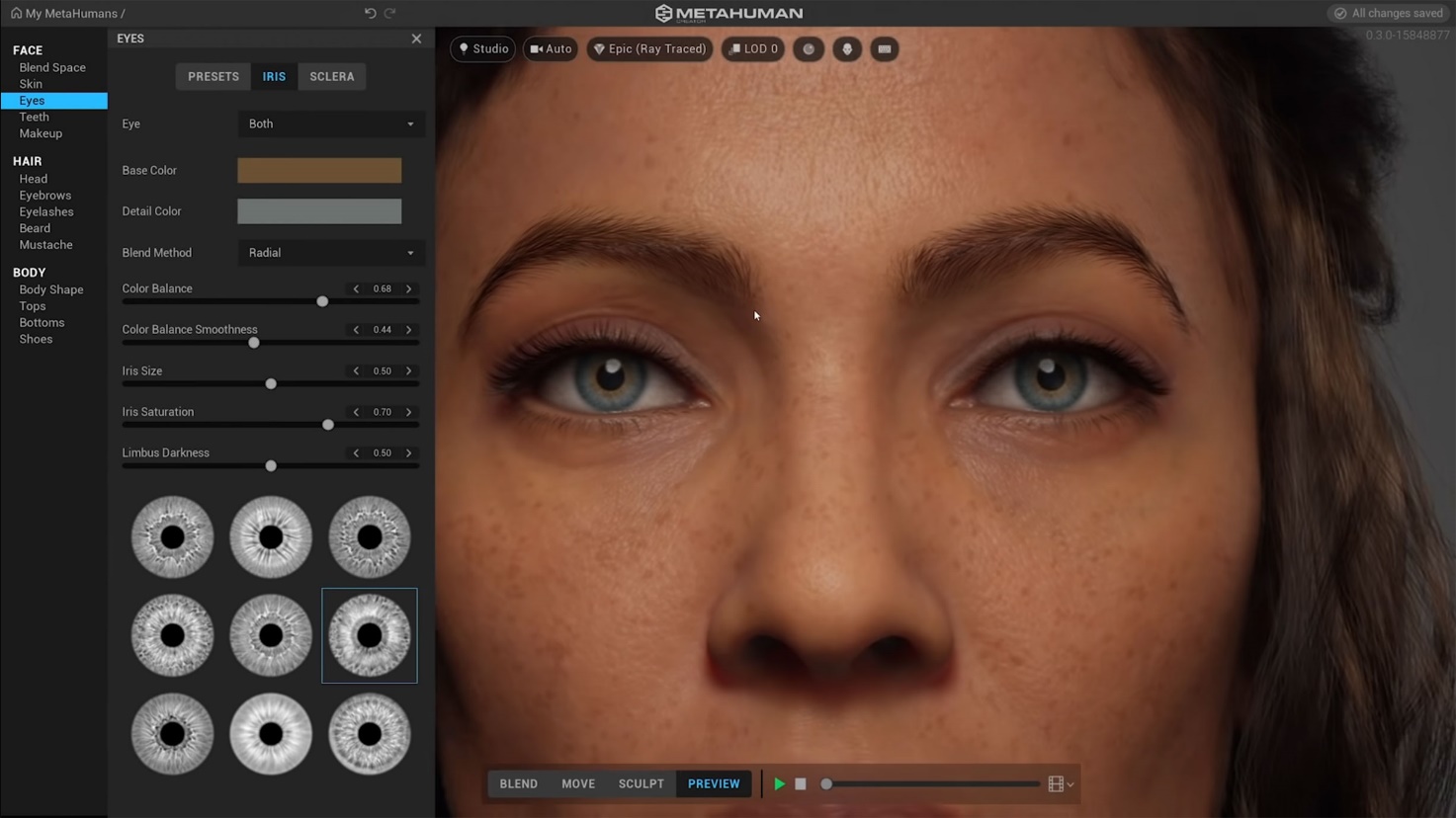
Moreover, cutting-edge technologies such as photogrammetry, Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs), and Volume Capture have further accelerated the production timelines. These technologies enable the quick and accurate capture of real-world elements, facilitating the creation of virtual assets and environments with unprecedented realism.
In summary, virtual production and the use of Unreal Engine have undergone a remarkable transformation, offering a host of tools and features that significantly impact the storytelling process. The newfound ease of use, high-fidelity rendering, inter-operability, and advancements in digital human technology and data handling have collectively revolutionized the way projects are developed and executed. The ability to achieve stunning results more efficiently has not only enhanced creativity but has also reduced production timelines, making virtual production an indispensable part of the filmmaking process.
One fascinating aspect of virtual production (VP) is how it has strategically positioned itself within the Production Plan. This innovative approach has compelled all stakeholders in the Film Creative Departments to establish a clear vision of their creative objectives well in advance of the shoot. As a result, it facilitates more efficient planning and execution of creative ideas, significantly reducing the need for extensive post-production fixes. VP encourages a proactive and collaborative workflow, ensuring that the desired outcomes are achieved with greater precision and effectiveness during the actual production phase.
AG: Can you share some of the most significant projects or productions you have been involved in during your years of experience? What made those projects stand out?
During my 18 years of experience in the Animation, VFX, and Film industry, I can’t say, I have had an extensive exposure to Virtual Production in its current form. However, there are a couple of significant projects that stand out, showcasing the cutting-edge technology and creative challenges in virtual production.

One of the most noteworthy projects I was involved in was the iconic "Lion King." This production utilized virtual production extensively for previsualization and post visualization, effectively creating the entire film during those stages. The use of cutting-edge tech in virtual production allowed us to visualize and refine the scenes with incredible detail and precision, making it a truly transformative experience.
Another remarkable project I had the privilege of briefly being part of during the preparation stages was a period piece directed by a renowned Hollywood Director. The challenge was to recreate an entire city from the Roman times, demanding immense scale and attention to detail. Employing various techniques and pushing the boundaries of virtual production, we sought to achieve a level of authenticity that was both visually stunning and historically accurate.
With each project, I continue to learn and adapt to the ever-evolving virtual production technology. As the field progresses, we are discovering new and innovative ways to tackle creative challenges, paving the way for even more exciting opportunities in the future.
While my experience with virtual production may not be extensive yet, I eagerly look forward to the projects that lie ahead, where I can contribute my skills and witness the ongoing evolution of this dynamic and transformative technology. As virtual production continues to evolve, I anticipate being part of projects that redefine the boundaries of visual storytelling and expand the possibilities in the world of filmmaking. With each step forward, I am confident that I will have more compelling stories to share about my involvement in the virtual production realm.
AG: What are the key skills and expertise required to be a successful on set supervisor (Virtual Production)?
Virtual Production Tools and Technology: As an on-set supervisor, a deep understanding of virtual production tools and technologies, especially those related to Unreal Engine or other real-time rendering platforms, is crucial. This includes expertise in using LED walls, Simulcam, motion capture systems, and virtual camera setups.
Cinematic and Technical Knowledge: A strong grasp of cinematography and camera techniques is essential to achieve the desired visual style and storytelling elements in virtual production. Knowledge of camera movements, framing, composition, and lighting is paramount.
Real-time Problem-Solving: On-set supervisors must have excellent real-time problem-solving skills. They need to address technical issues, optimize scenes for performance, and make quick decisions to maintain the production's momentum.
Collaborative and Communication Skills: Virtual production is a collaborative process involving multiple departments, from VFX and art direction to camera and lighting teams. Effective communication and collaboration skills are vital to convey the director's vision and coordinate efforts seamlessly.
Attention to Detail: The on-set supervisor must pay close attention to detail, ensuring that all virtual elements blend seamlessly with the live-action footage. This includes matching lighting, shadows, and camera angles to achieve a realistic and cohesive result.
Adaptability and Flexibility: Virtual production environments can be dynamic and unpredictable. Being adaptable and flexible to handle last-minute changes or new creative directions is essential.
Problem-solving in Hybrid Environments: In virtual production, on-set supervisors often work in hybrid environments, combining real sets with virtual elements. Understanding the challenges and opportunities of this setup is crucial.
Understanding the Filmmaking Process: A solid understanding of the overall filmmaking process, from pre-production to post-production, helps on-set supervisors anticipate potential issues and ensures a smoother production flow.
Leadership and Team Management: On-set supervisors may oversee a team of technicians and artists. Leadership skills are important to guide the team, delegate responsibilities, and maintain a positive working environment.
Creative Vision: To be successful, an on-set supervisor needs to not only understand the technical aspects but also have a creative vision aligned with the director's. This helps in making artistic decisions and achieving the intended emotional impact of the scenes.
Keeping Up with Technology: The virtual production landscape is continuously evolving. Staying updated with the latest advancements and industry trends is essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
By possessing these key skills and expertise, an on-set supervisor can effectively lead the virtual production team, contribute to the creative process, and ensure the successful integration of virtual elements with live-action footage to bring the director's vision to life on screen.
AG: How do you collaborate with directors, cinematographers, and other members of the production team to create virtual sets that align with their vision?
Virtual production can begin at various levels, and it often starts with a brief from the Director. In some cases, we may develop a previz that serves as a more comprehensive representation of a storyboard or animatic, providing the filmmaker with a clearer understanding of their intended shots. This previz stage also plays a crucial role in determining the most suitable methodologies to achieve each shot's desired effect.
Whether the approach involves capturing scenes directly on camera, rendering final pixels on an LED Wall, utilizing Simulcam technology with post compositing, or employing traditional VFX techniques, the real-time production pipeline offers remarkable flexibility and speed. This rapid iteration process allows all creatives involved to swiftly view results, enabling informed decisions on which elements to incorporate or discard, leaving very little to the imagination.
The real-time aspect of virtual production proves invaluable as it empowers the creative team to witness immediate outcomes, making it easier to select the most effective options to best realize the Director's vision. This seamless integration of creativity and technology greatly enhances the storytelling process, ultimately resulting in a more refined and immersive cinematic experience and most importantly making the production process more efficient.
AG: What are some of the challenges you have encountered while working in virtual production, and how have you overcome them? What process do you follow?
The continuous evolution of virtual production technology has resulted in limited awareness about its full potential and applications. It is essential to recognize that virtual production is not intended to replace traditional VFX but rather to enhance the overall production process by incorporating some post-production elements during the pre-production stage.
In many instances, film creatives have grown accustomed to working with ideas that may not be fully developed. Such ideas are often refined and experimented with during the production phase, leading to challenges when they are not adequately planned or executed due to time and budget constraints. Consequently, the expectation arises that these issues can be rectified magically in post-production, which places immense pressure on the post-production team and complicates the overall process.
Virtual production, while offering greater flexibility, demands significant preparation and commitment before entering the production phase. This requirement can be challenging to convince traditional film creatives to embrace fully. For example, showcasing the flexibility of moving set pieces when shooting on an LED Wall may appear straightforward in promotional materials, but in reality, it involves meticulous planning and coordination.
Various critical tasks, such as planning camera movements, frame rates and sync, setting up tracking systems, lens calibrations, and color calibrations, need to be planned/ accomplished before the shoot. However, at times, it proves difficult to allocate sufficient time for these essential pre-production processes, which can impact the overall success of the virtual production.
Overcoming these challenges requires a shift in mindset and a willingness to embrace the benefits of virtual production by dedicating time and resources to comprehensive planning and preparation. The integration of virtual production in the filmmaking process can lead to more efficient workflows, reduced pressure on post-production, and ultimately, a more seamless and immersive cinematic experience.
AG: How do you ensure the seamless integration of real actors and physical props with virtual sets? Are there any specific techniques or tools you utilize?
Ensuring the seamless integration of real actors and physical props with virtual sets in virtual production is crucial for creating a convincing and immersive visual experience. Several techniques and tools are utilized to achieve this level of integration:
Virtual Camera System: Virtual production often employs a virtual camera system that allows the director and cinematographer to view the virtual set in real-time from the perspective of the physical camera on set. This setup enables them to frame shots and compose scenes with precision, ensuring that the real actors and physical props are positioned correctly within the virtual environment.
Real-time Rendering: Advanced real-time rendering engines like Unreal Engine and Unity play a significant role in virtual production. They render virtual sets and elements in real-time, allowing actors and filmmakers to see the virtual world merged seamlessly with the live-action footage as they shoot, ensuring immediate feedback and adjustments.
LED Walls and Projection: LED walls and projection technology are used to display dynamic virtual backgrounds on set. These tools provide realistic lighting and reflections on actors and props, enhancing the integration between the real and virtual elements. By projecting virtual sets onto physical surfaces, the interaction between actors and the virtual environment becomes more tangible.
Real-time Tracking and Calibration: To ensure proper alignment between the virtual and physical elements, real-time tracking and calibration systems are employed. These technologies track the position and movement of the physical camera and actors, allowing the virtual environment to adapt accordingly.
Physical Markers and Tracking: Actors and props may wear physical markers or use tracking devices during the shoot. These markers aid in accurately capturing their movements and interactions, which is crucial for seamless integration in post-production.
Live Compositing and Keying: Live compositing and keying techniques are sometimes used on set to integrate real actors and physical props with the virtual environment in real-time. This allows filmmakers to visualize the final composite during the shoot, providing valuable reference for the overall scene.
Virtual Production Supervisors: Virtual production supervisors play a critical role in ensuring smooth integration. They liaise between the on-set crew, visual effects team, and the director, ensuring that everyone is on the same page and that the virtual elements align seamlessly with the live-action components.
Collaborative Approach: Achieving seamless integration requires a collaborative approach among various departments, including VFX, production design, cinematography, and costume design. Close communication and coordination are essential to maintain consistency between the real and virtual elements.
By employing these techniques and utilizing advanced real-time rendering tools, virtual production achieves a level of integration where real actors and physical props appear naturally immersed within the virtual sets, resulting in visually stunning and cohesive scenes on screen.

AG: What role does real-time rendering play in virtual production, and how does Unreal Engine/ Unity facilitate this process?
Real-time rendering plays a pivotal role in virtual production, revolutionizing the way filmmakers and content creators bring their visions to life. It enables the seamless integration of live-action footage with virtual elements, creating a cohesive and immersive visual experience on set in realtime.
Real-time rendering allows directors, cinematographers, and other creatives to see the combined result instantly, making quick decisions and adjustments during the production process.
Unreal Engine and Unity are two of the most popular real-time rendering engines used in virtual production, each with its unique strengths and features.
Unreal Engine:
Photorealism: Unreal Engine is renowned for its high-fidelity rendering capabilities, delivering photorealistic visuals with stunning details, realistic lighting, and impressive effects.
Photorealism: Unreal Engine is renowned for its high-fidelity rendering capabilities, delivering photorealistic visuals with stunning details, realistic lighting, and impressive effects.
Real-time Interactivity: It provides real-time interactivity, enabling creators to interact with and modify scenes on the fly, whether on set or during pre-visualization.
Seamless Integration: Unreal Engine easily integrates with other industry-standard software and hardware, allowing smooth collaboration and asset exchange throughout the production pipeline.
Virtual Camera: Unreal Engine offers a Virtual Camera system, enabling directors and cinematographers to preview shots from the perspective of the camera in the virtual environment.
LED Wall Technology: Unreal Engine plays a crucial role in powering LED Wall technology, where realistic virtual backgrounds are displayed on LED screens in real-time, providing interactive and dynamic environments for actors to perform in.
Both Unreal Engine and Unity have contributed significantly to advancing virtual production by providing accessible and efficient real-time rendering solutions. The ability to render complex scenes, including realistic virtual environments and digital characters, in real-time has revolutionized the filmmaking process and enriched the creative possibilities for directors, cinematographers, and visual effects artists alike.
AG: How do you stay updated and continually enhance your skills in virtual production? Are there any resources or communities you recommend?
Staying updated and continually enhancing my skills in virtual production is a dynamic and ongoing process. My passion for filmmaking acts as a driving force, constantly pushing me to learn and explore new possibilities. Additionally, the presence of younger peers who effortlessly embrace and adapt to new technologies serves as a constant motivation, reminding me to remain relevant and avoid being left behind.
To keep myself abreast of the latest trends and developments in virtual production, I frequently turn to YouTube, which offers a vast array of tutorial videos shared by the community. These videos provide valuable insights and practical knowledge that I can apply in my work.
In addition to YouTube, I actively participate in community channels on platforms such as Slack and Discord. These virtual production communities foster a collaborative environment where likeminded professionals share their experiences, exchange ideas, and offer valuable advice. Engaging with these communities provides me with valuable networking opportunities and keeps me connected with the industry's latest advancements.
I am committed to dedicating a few hours each day after work to read, watch, or create something related to virtual production. This consistent practice allows me to continually refine my skills and expand my knowledge in this rapidly evolving field.
As a VP Supervisor, my role is to offer effective solutions to creative challenges, making it essential for me to be well-informed and equipped to execute ideas efficiently. By maintaining an active learning approach and engaging with the virtual production community, I can stay at the forefront of this exciting industry and deliver the best possible outcomes for the projects I work on.
AG: What advice would you give to someone aspiring to pursue a career in virtual production?
For aspiring individuals looking to pursue a career in virtual production, the current technological advancements offer incredible opportunities to create efficiently and explore multiple creative options. However, with this empowerment comes a greater responsibility for creatives to possess a strong grasp of their craft and make well-informed decisions that align with the vision of their work.
Embracing virtual production technology allows more people to participate and create at a faster pace than ever before. In this context, it becomes essential to strike a balance between artistic proficiency and a deep understanding of the technical aspects involved in the process. It is not uncommon to witness virtual production artists getting caught up in the intricacies of the technology, sometimes losing sight of the primary objective – to achieve believable and captivating shots or sequences that complement the overall storytelling in a film.
To succeed in the field of virtual production, aspiring professionals should focus on honing their artistic abilities and storytelling skills. Understanding how to use the technology as a means to enhance creativity and efficiently bring ideas to life is vital. Continuous learning and keeping up with the latest advancements in virtual production tools will be instrumental in maintaining a competitive edge.
Collaboration and teamwork are also crucial in virtual production environments. Being able to effectively communicate with other creatives, such as directors, cinematographers, and production designers, will foster a cohesive and successful creative process.
Additionally, seeking guidance and mentorship from experienced professionals in the virtual production industry can be invaluable for learning best practices and gaining insights into realworld challenges and solutions.
Ultimately, the key advice for aspiring virtual production professionals is to embrace both the artistic and technical aspects of the field. Combining creativity with a solid understanding of the technology will empower them to produce compelling and visually stunning work that adds value to the storytelling process in the world of filmmaking.
AG: Looking ahead, what do you envision for the future of virtual production? Are there any exciting developments or possibilities that you are particularly excited about?
Looking ahead, the future of virtual production is incredibly promising, driven by its goal to empower all creatives rather than replace traditional practices. The integration of multiple AI tools into the virtual production pipeline will lead to even greater sophistication and efficiency in the process. While there may be an initial period of clutter and experimentation, it will undoubtedly pave the way for streamlining and refining the technology's capabilities.
We are entering a defining moment in time, as trends and techniques for content consumption are rapidly changing. Virtual production will emerge as a significant medium that facilitates the execution of complex ideas with much greater ease and flexibility than ever before. Exciting developments already, include the creation of set designs and digital humans using scans from smartphone cameras, sensorless mocap technologies, and AI-driven tools for geometry creation that can handle millions of polygons, intricate hair, cloth, crowd simulations, and special effects systems. Additionally, hyper-realistic rendering capabilities are consistently improving, thanks to the rapid advancement of computing power.
As these technologies continue to advance and become more accessible, virtual production will democratize creative expression and provide new opportunities for filmmakers, animators, and visual effects artists. The merging of AI and virtual production will not only streamline the creative process but also unlock new realms of artistic possibility, pushing the boundaries of storytelling and visual experiences.
In summary, the future of virtual production is bright, and the prospects for innovation and creativity are boundless. As AI and virtual production technologies evolve in tandem, the industry will witness a transformative shift that empowers creatives to bring their visions to life in ways previously unimagined.
As Subhankar paves the way for accelerating film production and expanding the horizon for imagining stories on screen we bid Shubie ‘bie bie’.
You can reach out to him through these channels
You can reach out to him through these channels

